What is Marijuana ?
When we hear the word “marijuana,” the things that come out of our mind are weeds, drugs, addiction, abuse, heavenly feeling.
Users claim that they feel every good thing in this world when they are under the influence of this plant. But people in general see all the negative sort of things in this plant because of what it does to the user, well, when it is abused. Despite of this, there are claims that marijuana has medical benefits. How can this plant be useful in the medical field? Let’s find out in this article.
Marijuana Plant
History says the marijuana plant came from the Chinese. But it is believed that it is an Indian native which can be found in the northern part of Himalayan mountains. Certainly, it cannot be found everywhere because planting and possessing the plant is forbidden by the laws of almost every country.
The marijuana plant grows 13 to 18 feet or 4 to 5.4 meters. Have you ever heard of hashish? This is also a psychoactive drug wherein marijuana’s resin is the plant derivative.
The stalk of the marijuana plant has its own legal uses. It can be used to create different kinds of fabrics, ship sails, paper, oil for varnishes and paints. It can also be used as a food ingredient. Actually, its seed is high in carbohydrates and proteins. [1]
Picture 1 : The marijuana leaf with 5-7 leaflets joined at the centerpoint.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids refer to the active chemicals in the marijuana plant that cause psychoactive effects. Marijuana plant has been found to contain over 480 natural components and 66 of which are considered as cannabinoids [2].
Subclasses of Cannabinoids
- Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC)
This is the main chemical in the marijuana plant which causes its psychoactive effects. Its effects to the user’s body include euphoria, stimulation, muscle relaxation, bronchodilation, hypotension, analgesia, anti-inflammation, anti-epilepsy, anti-emesis, anti-depression, and increase in appetite. Other subclasses have synergistic and antagonistic effects with this chemical. [3]
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
Cannabigerol is not known to be causing the psychoactive effects of marijuana. This component can be used medically in glaucoma patients because it relieves intraocular pressure (IOP) [4]. This also has sedative and antimicrobial properties [3].
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
Cannabichromene has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties [5].
- Cannabidiol (CBD)
Medically speaking, this is a good cannabinoid and it’s good that its abundance in marijuana resin reaches 40%. Cannabidiol does not cause the psychoactive effects of marijuana, instead it reduces these disturbing effects. This means that the higher the CBD, the lower the potency of the marijuana plant [2]. Evidences show that CBD has medical benefits to patients with schizophrenia, anxiety disorders, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis spasms, nausea, and even cancer [6].
- Cannabinol (CBN)
When THC is oxidized, cannabinol forms. CBN is a weak psychoactive drug. It reduces the effectiveness or potency of THC. [2]
- Other Cannabinoids such as
- Cannabinodiol (CBDL)
- Cannabicyclol (CBL)
- Cannabielsoin (CBE)
- Cannabitriol (CBT)
Marijuana Varieties and Strains
There are numerous Cannabis varieties and strains. Some are pure breed and some are hybrids. Its medical benefits depend on the needs of the user. [7]
Main types of Cannabis.
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Pure Cannabis Sativa
Cannabis sativa’s purity causes paranoia and arrhythmia (irregular heartbeats) so this is rarely used in the medical field. Examples include
- Acapulco
- Burmese
- Malawi Gold
Hybrid Sativas
This may be a combination of two or more types of Cannabis sativa or a combination of Cannabis sativa and indica wherein the percentage component of the former is higher. Unlilke pure sativa, hybrid sativas do not cause paranoia. It is used as an antidepressant and appetite stimulant. Examples include
- Haze
- Willy Nelson
- Jack Herer
- Kali Mist
Pure Cannabis Indica
Cannabis indica is for patients who are in pain and who are suffering from insomnia. The most common examples are
- Hindu Kush
- Pakistani
- Herijuana
- Hashplant
- Afghani
- G-13
Hybrid Cannabis Indica
Hybrid Cannabis indica refer to the “kush” strains. This may be a combination of two or more types of Cannabis indica or a combination of Cannabis sativa and indica wherein the percentage component of the latter is higher. These are the strains that are mostly preferred in the medical field because they are ones that cater to the exact needs of the patient. A few examples of hybrid Cannabis indica include
- Purple Kush
- Blueberry
- Master Kush
- OG Kush
- Grapefruit
- White Rhino
- Northern Lights
- Romulan
- Dutch Treat
Preparations
Different preparations of using marijuana have been developed overtime. Different routes of administration have also been used. Though different in forms, these things contain the same ingredient, marijuana. [8]
Weed
This does not require a lot of preparation. You just have to dry the leaves and the buds of Cannabis sativa or indica plant. It is then ready to be used. It can be rolled into cigarettes or joints. It can be sprayed or mixed with other psychoactive drugs if the effect is not enough for the user. Burnt or not, weeds have a very strong pungent odor and the smell stays with every part of you for a long time, so it is easy to notice whether a person is smoking weed or not.
Picture : Marijuana Weed
Hashish
Other names include hash, pot, black, Moroccan, rocky, goldseal black, and redseal black. The resin is processed into an oily, solid bar with a dark yellow to black color. Its distinguishable pungent odor stays.
Picture : Marijuana Hashish
Hashish Oil
Of all the preparations, hashish oil is the most potent but least used form of marijuana. Even a slight amount of this could cause tremendous psychoactive effects on the user. This is being smoked or painted on cigarettes and joints.
Picture : Hashish Oil Marijuana
Foods and Drinks with Marijuana
Marijuana can be hidden through foods and drinks. Cookies and brownies are often used to mix marijuana with. For the drinks, milk is most preferred because of its demulcent texture, since marijuana is oil-based. However, marijuana’s presence in foods and drinks is not as easily detected as with the other preparations because its smell is not much noticed since the foods and drinks contain other ingredients which might mask marijuana’s pungent odor.
Marijuana Facts
- Marijuana is a drug classified under Schedule I. Drugs under this classification has no approved medical benefits. They are potentially hazardous and they cater substance abuse. Other examples of Schedule I drugs are heroin, LSD, ecstasy, methaqualone, and peyote. [9]
- There have been observed medical uses for marijuana though evidence is not enough. It is known to treat chronic pain, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and glaucoma. It also improves appetite of patients with AIDS, and it removes the nausea and vomiting side effect of chemotherapy in cancer patients. [10]
- In 2007, there was a study at San Francisco General Hospital showing that marijuana decreases neuropathic pain by 34%. [10]
- In 2011, another study at San Francisco General Hospital showed that marijuana added to opioid drugs decreases the pain at 27%. [10]
- In 2700 BC, it is known that a Chinese emperor named Shen Nung was the first person to prescribe marijuana as an herbal treatment. [10]
- History says that in 1800s, marijuana has been used to treat sexual dysfunctions and insomnia. [10]
- National Institute on Drug Abuse is the only agency authorized to have a formal research on marijuana. To do this, of course they have to cultivate the plant. The site is on the University of Mississippi. [10]
- Increase marijuana use equals lower intelligence. [10]
- Marijuana use is linked to numerous vehicle accidents and deaths. [10]
Marijuana Medical Uses
More often than not, medical marijuana is used for chronic conditions. Research states that the THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), which actually gives you the psychoactive effects of marijuana, is the same thing that alleviates the pain and suffering of some patients with [11]
- Cancer
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
- Epilepsy
- Multiple sclerosis
- Glaucoma
- Insomnia
- Crohn’s disease
- Migraine
- Arthritis
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Primary medical actions that marijuana does to the user’s body are: (a) relieves pain; (b) reduces nausea and vomiting (antiemetic); and (c) stimulates appetite [12]. How it works is not extensively stated but researchers believe that the THC binds with the endocannabinoid receptors, thereby diminishing the pain and anxiety that the person feels [11].
Effects of Marijuana on the User’s Body
Physiological Effects
THC is easily absorbed in the body and immediate effects can be felt by the user. Although the following are short-term effects, the components of marijuana stay in your system and the residual effects of being “high” may last for a month.
- Tachycardia or fast heart rate
- Increased blood pressure
- Tachypnea or fast breathing
- Red eyes
- Dry mouth
- Increased appetite
- Slow reaction time [13]
Psychological Effects
Like the physiological effects, the residual psychological effects of marijuana may last for days or weeks. The following are the psychological effects
- Euphoria
- Paranoia
- Time disorientation
- Anxiety
- Random thinking with magical ideas
- Memory loss
- Depression
- Calmness [13]
Medical Risks of Marijuana
- Smoking marijuana damages your respiratory passageway.
- The user’s respiratory tract will be less effective in defending against bacteria, viruses, and infections, which may pose a greater risk for patients with AIDS and cancer, since they are immunocompromised. [14]
- Immediate effect of marijuana use includes impairment in thinking, perception, judgment, learning, memory, and coordination. [14]
- Marijuana is believed to be a precursor of serious mental illnesses such as acute toxic psychosis, panic attacks, hallucinations, paranoia, depression, depersonalization, delusions, aggressive behavior, and flashbacks. [14]
- Marijuana causes infertility. Contrary to what others may think, it dimishes libido. It also marks down sperm count and quality. [13]
As you may notice, cancer, AIDS, etc. which are included in the medical uses, are also included in the medical risks. What marijuana does to cancer and AIDS patients is that it temporarily relieves the symptoms that the patients feel. That’s good. But the problem is the effect after the patient has used marijuana.
It poses a greater problem and greater risk in the part of the patient. It’s like marijuana as a medication is contraindicated to the very indications that it must treat. Clearly, the risks outweigh the benefits. There is a reason why marijuana is categorized as a Schedule I drug. There are countless medications that do not give extreme medical risks as marijuana does. There are so many options and alternatives. Why would you settle for something that could give less positive outcome and give more negative outcomes?
Marijuana Tests
Of all the tests in the world, drug test may be the hardest one to pass if you are a drug user. Taking in marijuana today doesn’t mean you can take it out of your system today. It may take days, weeks, and even months to get it out of your system. It depends on how long you have been using, how much you use, metabolism rate, drug potency, excretory factors, and body size.
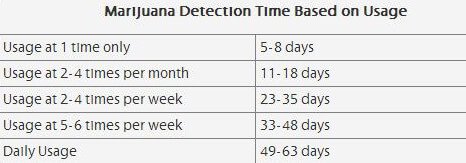
Depending on the route of administration, marijuana steadfastly invades the bloodstream. But it will not only be confined in the bloodstream. THC will be stored in our body fats. Overtime, our body naturally excretes it via urine or feces [15]. However, it will not be eliminated immediately. The approximate amount of time that marijuana stays in our body is presented in the table below [16].
Marijuana detection time depends on how long a person uses the marijuana, among other factors. Chronic users have longer detection times. The more you use it, the longer it stays in your body.
Table Source: marijuana.com
Typically, the THC metabolites in the bloodstream have an estimated elimination half life of 20 hours [15]. The ones that are stored in the body fat linger for about 10-13 days so the best answer to the question “How long is marijuana detectable in your body?” is 13 days [15]. However, this may be a short number of days when the person is a frequent or daily user of marijuana.
More often than not, urine specimen is used for drug tests. It is because what you excrete reflects what’s inside your body. Laboratory examination called enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique (EMIT) or radioimmunoassay (RIA) is done. When the result turns out to be positive, it will be confirmed using gas chromatograph mass spectrometer (GCMS) to ensure that it is not a false positive result. [15]
Marijuana Addiction and Abuse
Not all marijuana users become addicted to it. Some are able to control themselves. But unfortunately, not everybody can do this. Some just can’t get enough of being “high.” Chronic use of marijuana will lead to addiction and abuse little by little, and eventually the user might even be psychologically dependent on it. An estimate of 9% of marijuana users will be dependent on it [17]. This percentage increases with how long you have been using, how much you use, and when you started using it.
Here are the 10 signs of marijuana addiction.
- Marijuana Tolerance, Dependence, and Withdrawal
When a person is addicted to marijuana, he just can’t get enough of it. When he becomes a chronic user, his initial dose when he first took it won’t seem to be enough. So as the time goes by, the dosage and frequency will increase (tolerance), to the point that he thinks he cannot function well (dependence) without marijuana in his system. Absence of marijuana will show withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, insomnia, loss of appetite, and aggressive behavior.
- Using more marijuana than intended
- Unable to quit marijuana use
- Spending most of the time getting high
- Reduced usual productive activities of daily living
- Using marijuana despite of encountering huge problems it causes
- Using marijuana to escape from the real world and forget problems
- Use of marijuana as your pleasure and center of your life
- Denying and ignoring comments about him that he has changed
- Will do everything just to get himself a marijuana
Being addictive to marijuana and other drugs is very difficult to get by. It will be so much more difficult than you can ever imagine. So before it starts, be good to yourself. Do not use marijuana. Do not even try it. Because that one try can change your life forever. [18][19]
Rehabilitation and Treatment
The first thing that you should do is motivate yourself to stop. Inspire yourself of all the good things life can give you. Think of yourself, your future, your family. Compare what life will be with or without marijuana. Determination and discipline will stop you from using marijuana. Without self-help, there is nothing we can do.
After that, seek outside help. There are many marijuana rehabilitation centers in the world. There is no medication for this. Detoxification is a must, and only you can truly help yourself by quitting marijuana completely. It will be hard because of the withdrawal symptoms, yes, but many people have done it, and so can you.
Psychosocial treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy, community reinforcement, contingency reinforcement, and support system [20] are very helpful for ex-marijuana users. You might think that these treatments will do nothing to you, but you are so wrong. These are proven to be truly effective. Talk to anybody who you think can help you get over this addiction. Get help and I promise, it will be worth it.
References
- http://www.howstuffworks.com/marijuana1.htm
- http://adai.uw.edu/marijuana/factsheets/cannabinoids.htm
- http://www.canadamedicalmarijuana.com/medical-marijuana-strains.html
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabigerol
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabichromene
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabidiol
- http://medicalmarijuana.ca/learning-center/marijuana-strains
- http://addictions.about.com/od/legalissues/tp/Types-Of-Marijuana.htm
- http://www.justice.gov/dea/druginfo/ds.shtml
- http://www.huffingtonpost.com/glenn-d-braunstein-md/marijuana-facts-fiction_b_2575507.html
- http://curiosity.discovery.com/question/whats-medical-marijuana-for
- http://www.ncsl.org/issues-research/health/state-medical-marijuana-laws.aspx
- http://www.webmd.com/mental-health/marijuana-use-and-its-effects
- http://cyber.law.harvard.edu/evidence99/marijuana/Health_1.html
- http://alcoholism.about.com/od/pot/a/marijuana_test.htm
- http://www.marijuana.com/news/drug-test/detection-time/
- http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/marijuana-abuse/marijuana-addictive
- http://thecyn.com/blog/10-signs-of-marijuana-addiction/
- http://alcoholism.about.com/od/pot/a/pot_addiction.htm
- http://www.drug-rehabs.com/marijuana.htm