Bronchospasm is a condition that describes the narrowing of the airway, which directly affects your breathing. The bronchi (muscles lining the airways) in the lungs tighten leading to narrowing of the airways.
As a result, the amount of oxygen that enters the blood is restricted. Even the amount of carbon dioxide that leaves the blood is restricted too. (1, 2)
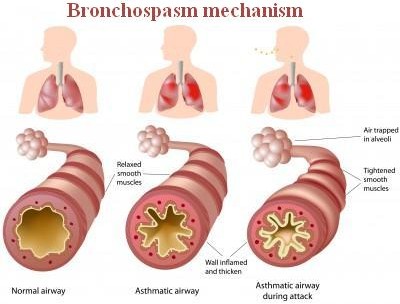
Photo 1: It shows a comparison image of a normal airway and an airway during bronchospasm.
Image Source: www.normalbreathing.com
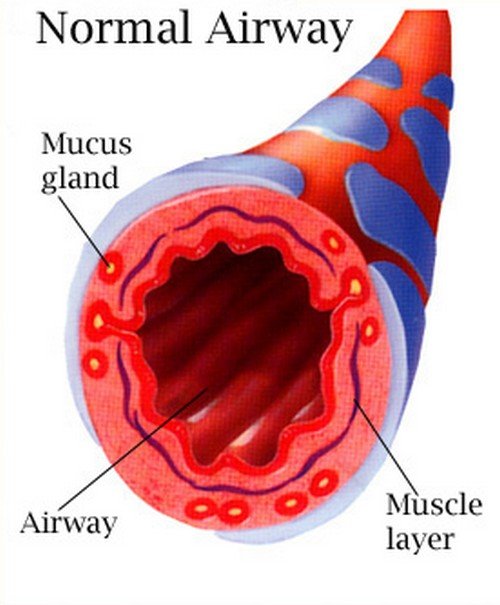 Image 2: A clinical presentation of a health airway.
Image 2: A clinical presentation of a health airway.
Photo Source: getasthmahelp.org
 Photo 3: Widening the airway using inhaled bronchodilators
Photo 3: Widening the airway using inhaled bronchodilators
Picture Source: healz.in
Symptoms of bronchial spasms
Signs of bronchospasm include the following:
- Difficulty breathing, especially at night, in the morning, and after performing strenuous activities
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- A wheezing sound when breathing
- Pressure and tightness in the chest area
- Fatigue (1, 2,3)
Causes of bronchospasm
- Upper respiratory infection
- Family history of asthma or allergic reaction to dust, mold, latex, pollen, and food additives
- Strenuous activities
- Environmental pollution such as smoke and strong odor
- Side effects of medications, especially aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, blood pressure medicines, and antibiotics
- Environmental factors such as dry and cold environment can constrict the airways, which makes it extremely difficult for you to breathe.
- Clinical negligence in handling anesthesia.
- Inflammation of the airway causing the airway to constrict and triggers bronchospasm.
- Stress and emotional distress (4, 5)
How long do bronchial spasms last?
A bronchospasm episode usually last for seven to 14 days. (5)
Bronchospasm vs Asthma
Is bronchospasm and asthma the same? Bronchospasm is the actual condition of the lungs while asthma is a clinical condition. Bronchospasm is one of the clinical manifestations of asthma. (6)
Difference between acute and paradoxical bronchospasm?
Acute bronchospasm refers to the spasmodic contraction of the bronchiole’s smooth muscles. The typical clinical manifestations include cough, shortness of breath, and wheezing sounds when breathing. On the other hand, paradoxical bronchospasm is caused by certain drugs.
One of the medicines that trigger paradoxical bronchospasm is albuterol. As you know, albuterol is used to treat bronchospasm, but it has adverse effect to the patient. It is a potentially life threatening condition. Therefore, patients should be closely monitored when taking albuterol and other drugs with the same side effects. (4, 5, 8 and 10)
How to diagnose bronchospasm?
A thorough examination will be done. The health care provider will take out information from you, especially your past medical and surgical history. A physical examination is done paying particular attention to your breathing.
Laboratory studies and diagnostic procedures should be done, which include:
- Chest x-ray – This is to thoroughly visualize the lungs and watch for any signs of infection, specifically upper respiratory tract infection.
- CT scan/CAT scan – A photo of the lungs is taken using a computer tomography. This test will assess the general condition of the lungs, especially if there are blood clots.
- Pulmonary function test – This is to detect the function of the lungs. It measures the strength of breathing upon exhalation.
- Lung volume test – It measures the amount of oxygen your lungs can hold.
- Spirometry – This test uses a spirometer, which measures the force of the air that you breathe in and out. (5, 6)
- Pulse oximetry – It is a device clipped onto the finger. It is used to measure the level of oxygen in the blood.
- Lung diffusion capacity – a tube is used to breathe in and out. It is used to see how well the oxygen gets into the blood stream.
- Eucapnic voluntary hyperventilation – This is used to detect exercised induced bronchospasm. What is exercise induced bronchospasm? It is a bronchospasm triggered by strenuous exercise. To avoid this condition, you should take short acting bronchodilator before exercising. (6, 7,8)
Treatment for bronchospasm
There are various methods for bronchospasm treatment. A pulmonologist (lung doctor) will thoroughly assess your health condition and will determine the right treatment approach.
The goal is to widen your airway so that you can breathe easily. Treatments for bronchospasm include the following:
- Bronchodilators – They make your breathing easy by expanding your airway. They also prevent future spasms. For quick relief of bronchospasm, the doctor prescribes a short acting bronchodilator. It widens the airways in just a few minutes. The therapeutic effect lasts up to four minutes. On the other hand, long acting bronchodilators’s therapeutic effect can last up to 12 hours. The only reason why it is not prescribe for acute bronchospasm if because it takes longer to start working.
- Inhaled steroids – They are used for long term management of bronchospasm. It alleviates swelling of the airways. Just like long acting bronchodilators, inhaled steroids take longer to start working.
- IV steroids/oral steroids – They are prescribed for severe bronchospasm.
- Antibiotics – In some instances, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics if he noticed an infection.
- Anticholinergics – They help relax and open the airway. (7, 8, 9,10)
What to do to prevent bronchospasms?
- You should avoid the things that can trigger bronchospasms.
- Before performing strenuous activities, you should warm up first. Your health care provider will create the best exercise plan for you.
- Those with bronchospasms may get infection easily. So, you should avoid sick people. There might be a need for you to have a flu vaccine.
- If you are in a dry and cold weather, practice breathing though your nose to warm the air before it gets to your lungs. This helps reduce lung irritation.
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water to loosen the mucus in your chest.
- Stay inside your home if the weather is too cold.
- Do not smoke. Avoid anyone who smokes.
- If you are senior, you should regularly see your doctor. Make sure that your influenza vaccine is up to date. (2, 5, 6,9)
When you should see your doctor?
If you have been coughing for quite a while now and doesn’t seem to go, then you should see your doctor.
The same thing goes if you have fever, worsening of wheezing sound, shortness of breath, spitting up blood, chest tightness, rapid and uneven heartbeat, and blue toenails or fingernails. (10)
Bronchospasm treatment at home
There are natural remedies for bronchospasm. They include the following:
- Butyeko Breathing Technique – It helps you breathe easier through shallow breathing exercises. This technique is based on the theory that short breathing raises the level of carbon dioxide in the body, which dilates the airways of the lungs.
- Increase your intake of foods rich in omega fatty acids – Omega fatty acid helps reduce the level of arachidonic acid in the body. Research showed that an increased level of arachidonic acid in the blood increases bronchospasm episode. Foods rich in arachidonic acid are meat, egg yolk, and shell fish.
- Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables – Bronchospasm episode is lower in people who love to eat fruits and veggies, especially carrots, tomatoes, and leafy greens. Butterbur, an herb native in Asia, Europe, and USA contains petasin and isopetasin. These compounds play an important role in reducing the inflammation of the bronchi. However, it should be used cautiously because too much of butterbur could cause headache, nausea with or without vomiting. Fruits like pineapple contain bromelain, a substance known for its anti-inflammatory property. It helps reduce the symptoms of bronchospasms.
- Weight loss – You should maintain a healthy weight to lower the episode of bronchial asthma.
- Relaxing activities – Stress triggers bronchospasms. You can benefit a lot from relaxing activities such as yoga. (1, 4, 6,9)
References:
- http://www.doctorshealthpress.com
- https://en.wikipedia.org
- www.healthline.com
- www.drugs.com
- www.healthcentral.com
- www.normalbreathing.com
- www.medicinenet.com
- www.epainassist.com
- www.healthresource4u.com
- Drug-induced Diseases: Prevention, Detection, and Management By James E. Tisdale
