What does Mordant mean ? Definition
A mordant is a substance useful in microbiology. It is being added to a stain to give color to different kinds of organisms.
With the use of mordant in microbiology, organisms are thoroughly and accurately identified. The definition of mordant is a chemical that keeps the dye in place.
There are various types of organisms. In a microbiology study, it is a must to correctly identify various type of organisms.
A staining procedure is done to add various colors to various organisms. The stains are chemicals of varying colors or also known as mordant. The microbiologist add mordant to identify the organism. The mordant does not stick to the organisms. (1, 2, 3)
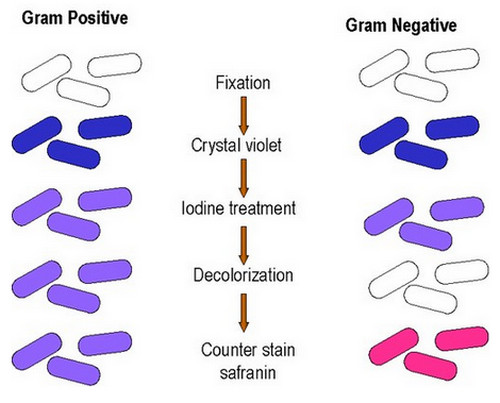
Image 1: A gram staining procedure outlining the color of the organism in various phases of the procedure.
Picture Source: 2.bp.blogspot.com

Photo 2: A typical mordant used in gram staining.
Picture Source: www.scienceprofonline.com
What is the function of a mordant?
The mordant holds down the molecule of a stain onto the microorganism. Anything that holds down a dye, be it a metal ion or halide ion can be classified as mordant. However, there are some mordants that bind on the dye as well as proteins of the microorganism.
There are various types of mordants, but the one typically used is ion because its electrical charge gets in contact with the electrical charge of a chemical dye. A large complex is created when the ion binds the dye, which is highly beneficial during the staining procedure. To see to it that the only true staining regions is seen, the staining procedure should be followed up by washing. (2, 3, 4)
Natural mordants for dyeing
There are different types of mordants and each type will give a different result. Some of the common types of mordent for natural dyeing include the following:
- Alum – It is the commonly used mordant. It should be used with care because it can give a sticky feeling that does not come out.
- Copper – It brings out the greens in dyes. It is more like the same as using tin, but it is less harmful.
- Chrome – It brightens the color of the dye. It should be used with utmost care because it can be extremely toxic. Gloves should be worn when handling chrome. It shouldn’t be inhaled. Left over mordant should be disposed properly because it is considered a hazardous waste. (3)
- Iron – It darkens the color of the dye. It should be used minimally because too much could make the fiber brittle.
- Glaubersalt – It is used as a natural dye and a chemical dye.
- Spectralite – It is used as a reducing agent for indigo dyeing.
- Tara Powder – It is a natural tannin product and is used for darker color.
- Tartaric Acid – It expands the cochineal color.
- Tin (Stannous Chloride) – It is useful in protein fiber as it gives extra bright colors to yellow, orange, and red. However, tin is rarely used in cellulose fiber.
Calcium Carbonate – It is used to lower the acidity of a dye bath. (4, 5)
Gram Stain Mordant
Gram staining is a method used by microbiologist to differentiate gram positive bacteria from gram negative bacteria. Gram staining is used along with culture of the material to correctly identify the cause of bacterial infection. Gram staining provides preliminary result whether the bacteria is present, including the type, shape, and characteristic.
To distinguish whether the organism is gram positive or gram negative, a color or dye is added. A gram positive bacteria would result to a violet stain because of the thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell walls. On the other hand, gram negative bacteria results in a red stain primarily because of the thin peptidoglycan wall.
The purpose of mordant in gram staining is to determine what type of microbe is causing the infection. The finding is sufficient enough to allow the doctor to come up with the right antibiotic prescription. Although, more test should be performed to thoroughly get rid of the infection. (5, 6, 7, 8)
Gram staining can also be ordered as a part of the culture evaluation. There are instances when a bacteria grow in a nutrient media in the lab. Gram staining is done to find out the type of bacteria present and to determine what other tests should be done to identify the root cause of infection. Gram staining does not only help identify the bacteria, but as well as fungi and yeast.
In a gram staining procedure, a crystal violet dye is used. Iodine is used a mordant and a 95% ethanol is used as a decolorizer. A 25% acetone or75% isopropanol can also be used. A gram safranin is used as a secondary dye. A gram positive bacteria yields to a purple color while a gram negative bacteria yields to a red color. (6, 7, 9)
The purpose of gram staining is to determine the composition of the cellular wall. The entire gram staining process may only take a few minutes. The process begins by adding a primary dye to the bacteria.
A mordant in the form of iodine is added to chemically change the shape of the molecule and trap it in the cellular wall. To add contrast to the cells, a decolorizer is used followed by a second dye. A gram positive cell is purple in color while a gram negative cell is red in color.
Aside from gram staining, there are other staining methods available. Various dyes are used to differentiate the parts of the bacteria structure such as spores, capsules, granules, and flagella. Staining techniques are highly beneficial in the microbiology study.
Staining is beneficial in cases where components of a microorganism is difficult to see under a microscope. Some microorganisms like rickettsia, mycobacteria, and spirochetes cannot be visualized using gram staining. Hence, a special staining procedure is done. (5, 6, 10, 11)
References:
- https://serc.carleton.edu
- sciencing.com
- www.uphs.upenn.edu
- https://en.wikipedia.org
- www.microscopemaster.com
- www.reference.com
- www.coursehero.com
- www.proprofs.com
- www.microbiologyinfo.com
- microbeonline.com
- www.generalmicroscience.com