The intercostal muscle is one of the important muscles in the upper cavity. It plays a huge role in stabilizing the upper body and aid in breathing.
The intercostal muscles have three layers: the external, internal, and innermost layer. Because of some activities and health practices, the layers of the intercostal muscles are strained to cause a variety of health issues. (1, 2, 3)
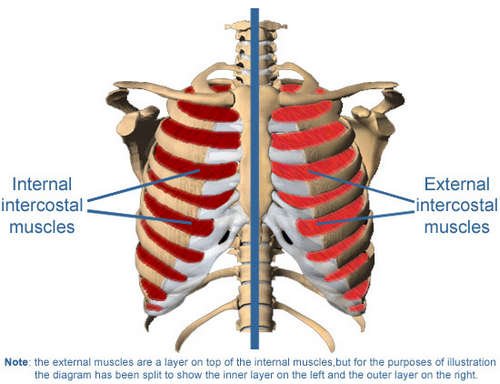
Image 1: An anatomy of the intercostal muscles, the muscles found in between the ribs.
Picture Source: digikalla.info
What are intercostal muscle strain symptoms?
- Upper back pain that is sharp in nature
- The pain becomes intense when you try to stretch or twist the muscles or when you cough, sneeze or breathe deeply.
- Muscle spasm and tension
- The area between the ribs is tender to the touch.
- Difficulty of breathing as manifested by a small and shallow sip of air.
- An obvious swelling in between and around the ribs.
- The pain gets intense with repetitive movements such as swimming and other forms of strenuous activities. (2, 3, 4, 5)
What causes intercostal muscle strain?
- Injury to the ribs secondary to sports (contact sports).
- Direct blow to the ribcage such as in the case of a car accident and fall.
- Twisting of the muscles while lifting heavy objects such as in the case of weightlifters.
- An intercostal muscle strain as a result of extreme yoga posture, dance position, playing games that require forceful twists such as tennis and golf. (4, 5, 6)
When is the best time to consult your doctor?
You need to carefully observe the extent of the injury, especially if the pain gets severe as time passes by. If the pain is bothersome, to the point of hindering you from performing your day to day activities, then it is high time to consult your doctor.
Intercostal muscle strain diagnosis
The doctor will conduct a series of test to accurately diagnose the condition of the patient.
- Physical exam – The doctor will conduct a thorough physical exam to detect any problems in the patient’s range of motion as well as to assess the severity of tenderness in the intercostal areas.
- History taking – The doctor will ask for the patient’s past medical and surgical history. Recent activities of the patient will also be investigated.
- MRI/X-ray – it is done to detect the presence of internal injuries.
Depending on the result of the exam, the doctor will grade the severity of muscle strain using the following:
- Grade 1 – At least 5% of the muscle fiber is damaged and it would take a few weeks to see a significant improvement.
- Grade 2 – There is an extensive damage to the muscle fiber but not to the extent of rupture. It would take a few months for the muscle to heal completely.
- Grade 3 – There is a complete rupture of the muscle and it can only be fixed through a surgical procedure. (4, 6, 7, 8)
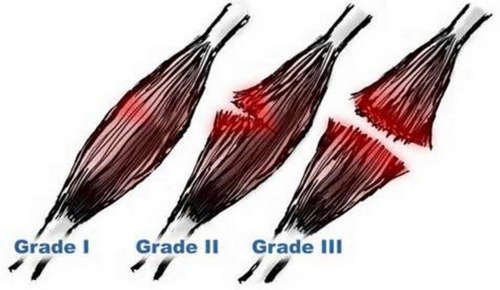
Picture 2: The grading system used for diagnosing intercostal muscle strain.
Photo Source: healthool.com
How long does it take for a strained intercostal muscle to heal?
The time needed for the muscles to heal completely depends on the severity or extent of the damage. It could take a few weeks to months. It also depends on the type of treatment and coping mechanisms the patients used. (7, 8)
Intercostal muscle strain treatment

Photo 3: Breathing and rehab exercises can significantly improve the condition of the patient.
Image Source: i.ytimg.com
The kind of treatment the patient needs depends on the extent of the damage and the overall condition of the patient. Some of the treatment modalities include:
- Pain reliever – for mild to moderate intercostal muscle strain, you can alleviate it using over the counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Just make sure you follow the drug’s usage instruction and to take pain reliever in full stomach to prevent irritation.
- Hot and cold compress – an alternate hot and cold compress can help alleviate the pain naturally.
- Breathing exercise – if you have an intercostal muscle strain, you will surely find it painful to breathe. Chances are you take shallow breaths, which could make you susceptible to infection and worst, pneumonia. You need to perform deep breathing exercise to significantly improve your condition. When breathing, you need to do it slowly but deeply and hold your breath for a few seconds. Do this at least ten times each session.
- Rest – You should limit your physical activity so as to prevent further damage to the intercostal muscles.
- Splitting – If you experience intercostal muscle pain when breathing, you need to splint the area by holding the pillow against the injured intercostal muscles.
- Physical therapy – A significant part of the treatment for intercostal muscle strain is physical therapy such as a foam roller exercise.
- Pain reliever injection – If the patient has tried all the treatment modalities mentioned above and the pain is still there, the last resort would be a pain reliever injection.
- Surgery – For third-degree intercostal muscle strain, the doctor would resort to surgery.
An intercostal muscle strain is something that should not be taken lightly. For mild strain, it usually heals on its own for a few days or weeks provided that it is well-rested and no further injury is added to the muscles. For moderate intercostal muscle strain, the healing would take a few weeks to a month whereas severe intercostal muscle strain takes longer to heal.
To prevent intercostal muscle strain, you need to perform warm up before performing strenuous activities. Take active measures to keep your muscles in perfect shape. It is also important to strictly adhere to your doctor’s order so as to hasten the healing time. Mild intercostal muscle strain can be treated at home with rest and mild pain reliever.
However, for moderate to severe intercostal muscle strain that is not responsive to over the counter pain reliever, the best thing to do is to consult your doctor the soonest time possible. (2, 5, 8, 9, 10)
References:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320925.php
- https://www.healthline.com/health/intercostal-muscle-strain
- https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/upper-back-pain/treating-intercostal-muscle-strain
- https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/upper-back-pain/intercostal-muscle-strain-symptoms-and-diagnosis
- https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/upper-back-pain/upper-back-pain-intercostal-muscle-strain
- https://body-motion.co.uk/injuries/mid-back-pain/intercostal-muscle-strain/
- https://www.physiotherapy-treatment.com/intercostal-muscle-strain.html
- https://www.rehabmypatient.com/ribs/intercostal-muscle-strain
- https://www.physioadvisor.com.au/injuries/upper-back-chest/intercostal-strain/
- https://www.epainassist.com/chest-pain/ribs/intercostal-muscle-sprain
