What is a brachioradialis muscle?
What does the brachioradialis do? Brachioradialis is one of the muscles in the forearms. It is also called Venke’s muscle. It extends from the lower part of the humerus down to the radius.
The humerus is the long bone in the upper arm and the radius is the long bone on thumb side of the forearm. Brachioradialis is both superficial and fusiform muscles.
Superficial muscles are located underneath skin and fat tissues while the fusiform muscles are skinny at their ends and thicker in the middle. They look like a spindle. (1, 2)
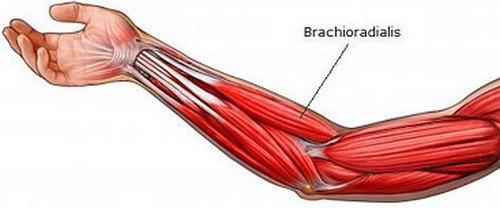
Image 1: The brachioradialis muscle situated in the forearm.
Picture Source: seannal.com

Photo 2: Outlining the different muscles of the arms.
Image Source: seannal.com

Image 3: The trigger point of brachioradialis muscle.
Picture Source: www.triggerpointtherapist.com
Functions of brachioradialis muscle
- Flexion of the forearm (raising the forearm by bending the elbow).
- Pronation of the forearm (rotating the forearm).
- Supination of the forearm (rotating the forearm so the palm faces up). (1, 2)
Brachioradialis Nerves
The muscles in the body are connected to a nerve, which supplies electrical impulses to the muscles from the brain. The radial nerve is the one that sends nerve impulses to the brachioradialis muscles. It is a large nerve consisting of nerve fiber from C5 to C7. These are the nerves originating from the neck region of the spinal cord.
However, if the muscles in the forearm become extremely tight, a shooting pain can be felt in the forearm and elbow. This is referred as brachioradialis pain. Brachioradialis pain after lifting heavy objects is common. There are instances when the pain extends to the back of the hand and into the thumb and index fingers. Brachioradialis pain and swelling are usually felt when shaking hands, turning a door knob, using a screwdriver, and drinking a cup of coffee. (3, 4, 5, 6)
What cause brachioradialis pain?
- Overexertion – It is one of the primary causes of brachioradialis pain. It is caused by overloading of the muscles for a long period of time. Eventually, the muscles become tender and painful. Manual labor could lead to overexertion of brachioradialis muscles and other surrounding muscles. Simple activities can also trigger brachioradialis pain such as typing on a computer for a long period of time and playing tennis. Frequent lifting, twisting, and holding things increase the stress in brachioradialis muscles.
- Trauma/injury – An injury or trauma to the arm can lead to brachioradialis pain. A sudden fall from a high place or a blunt force increase the possibility of brachioradialis pain. The pain is sharp and intense. (5, 6)
How to distinguish brachioradialis pain?
- A brachioradialis pain is felt along with muscle weakness.
- The onset of pain is sudden.
- The muscles of the arm get weak.
- The pain is described as sharp, radiating, and piercing.
- The origin of the pain is in the shoulder and upper arm.
- The pain is felt on one side of the body.
- The pain is felt on the front part of the elbow.
- The patient is unable to completely straighten or bend the elbow because the pain gets severe when attempting to do so.
- Simple activities intensify the pain.
- When the tendon or elbow is touched or moved, you will hear a crackling sound.
- The pain is temporarily relieved by pain killers but will recur again after a few hours.
- The shoulder muscles get weak. In severe cases, the shoulder muscles become paralyzed.
- The patient may complain of shortness of breath if the nerve near the diaphragm is affected. (6, 7, 8)
How to diagnose brachioradialis pain?
If you are experiencing brachioradialis pain, you should immediately consult your doctor. The doctor will conduct various diagnostic procedures and physical assessment to thoroughly check the condition of the patient.
The doctor will perform electromyography or nerve conduction studies to confirm the diagnosis of brachioradialis pain. It helps detect the extent of nerve damage. The strength and movement of the shoulders will be assessed too.
There are instances wherein the affected shoulders protrudes. Depending on the overall condition of the patient, the doctor will order for additional tests such as CT scan, MRI, and x-ray of the shoulders and neck. (8, 9, 10)
Brachioradialis Pain Treatment
A brachioradialis pain should be treated the soonest time possible. The focus of the treatment is to alleviate the pain, control the nerve damage, restoration of the functions of brachioradialis muscles, and improve the overall health. A brachioradialis tear can be improved using the right treatment modalities.
Rest
A painful brachioradialis muscle should be kept rested. After an injury, the muscle should be rested for at least 72 hours. You should apply ice with a 20-minute interval every two hours. This is to minimize swelling and inflammation. You should keep the affected area elevated, especially if it is caused by blunt injury. (3)
Brachioradialis Exercises
A brachioradialis tear can be improved using range of motion exercises. What are some exercises for brachioradialis? They include the following:
Isometric exercises
This involves contraction of the brachioradialis muscle for a specific timeframe. The patient should hold dumbbells while standing. Then, lift the weights at about three inches forward. Repeat the process until such time you will be able to see a significant improvement in your muscles. (1, 4)
Strength training exercises
Lifting heavy weights can help improve the condition of the brachioradialis muscle. However, you need to seek the advice of a physiotherapist to determine if you can now start lifting heavy weights. Exercises that target the brachioradialis muscles include hammer curl and reverse curl.
- Barbell curl – This is effective in training the brachioradialis muscles. Make sure that the weight of the barbell correlates with the strength of the arm muscles. The barbell should not be too light or too heavy.
- Dumbbell hammer curl – The barbell should be curled toward the shoulders. Performing dumbbell hammer curl exercise regularly will help regain the tone and tightness of the brachioradialis muscles minus the pain.
- Arm extension exercise – Keep the affected arm at the side and slowly straighten the elbow. Push down the forearm until such time you will feel a gentle stretch on the inside part of the elbow. (5, 8, 9)
References:
- https://www.belmarrahealth.com/brachioradialis-pain-symptoms-treatment-pain-relief-tips/
- https://www.muscle-joint-pain.com/trigger-points/trigger-point-self-treatment/brachioradialis/
- http://www.livestrong.com/article/486304-elbow-rehab-for-a-brachioradialis-strain/
- http://thewellnessdigest.com/brachioradialis-muscle-elbow-forearm-thumb-pain/
- https://safesymptoms.com/brachioradialis-pain/
- https://bodyspartan.com/bicep-tendinitis-and-brachioradialis-forearm-tendinitis/
- http://www.fitnessauthorityonline.com/brachioradialis-pain/
- http://www.triggerpoints.net/muscle/brachioradialis
- http://www.sportsinjuryclinic.net/anatomy/human-muscles/brachioradialis
- http://www.robertsonfamilychiro.com/brachioradialis-trigger-point.htm
