What is Facet Arthropathy ?
Facet arthropathy has been considered a leading cause of lower back pain for over 50 years. It rarely involves the spinal nerves but can cause great distress and discomfort.
The facet joints are those that help with the flexibility in the back. Their scientific name is zygapophyseal joints. The word arthropathy specifically means diseased joint. Therefore facet arthropathy is diseased facet joints found in the back and neck which can be noted with or without inflammation or swelling. It also does not include infection. (1,3,7)
In this article, you will read more about the facet joint anatomy, symptoms, causes, diagnosis process and treatments.
Facet joint Anatomy
The facet joints are true synovial joints and are made up of the following:
- Joint space
- Hyaline cartilage surfaces
- Synovial membrane
- Fibrous capsule
- Nerve fibers
- Substance P (inflammatory mediator) (1)
The following link shows a quick video with a good explanation of the anatomy of the facet joint: http://www.spine-health.com/video/facet-joints-video
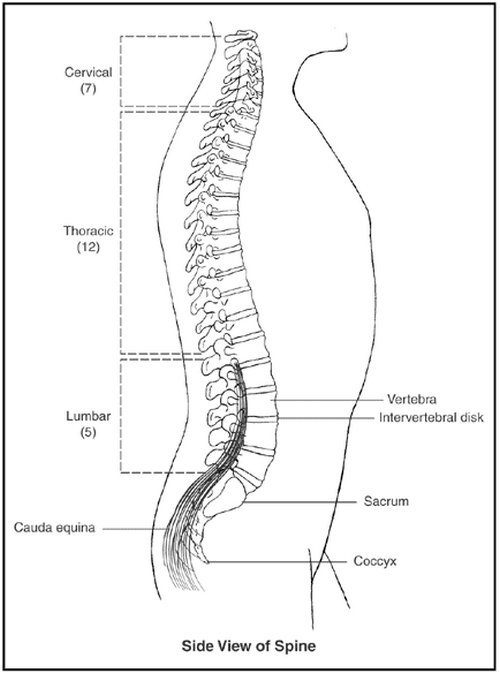 Figure 1 : A side view of the spinal bones and joints.
Figure 1 : A side view of the spinal bones and joints.
Image Source : www.niams.nih.gov
The initial studies of facet arthropathy were done by injecting saline into the facet cavity. This caused inflammation and similar pain to that experienced with arthropathy. Therefore assisting doctors to better diagnosis the issue at hand(11)
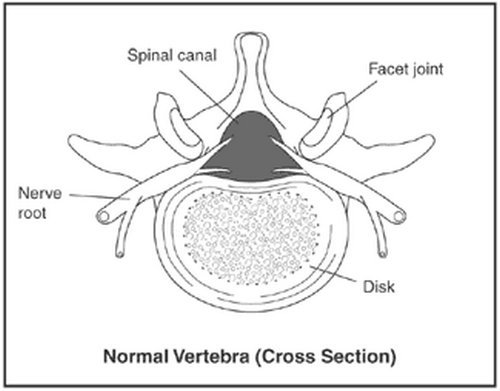 Image 2: The cross section view of a normal vertebra.
Image 2: The cross section view of a normal vertebra.
Photo Source : www.niams.nih.gov
Facet Arthropathy Symptoms
Lower back pain due to facet arthropathy is difficult to assess without using invasive techniques. But the following can be seen as common symptoms and may help with diagnosis:
- Pain located in the lower back which radiates into the knee.
- Usually, does not cause pain in the central back.
- Pain could even radiate past the knee
- Pain occurs a few times a month or as little as a few times per year
- Tenderness to touch
- Discomfort increases when bending backward more than when bending forward
- Pain episodes that are recurrent
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness or tingling in extremities
- In early stages may be noted as a stiffness in the mornings (1,3,4)
What is the difference between chronic and acute back pain?
- Acute pain– Will begin to subside without treatment or with basic medications such as acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen.
- Chronic pain– May or may not need surgery to go away. Usually does not get better with short term treatment and needs long-term physical therapy and behavioral changes.
How can a diagnosis be made?
Basically, your doctor will use the common symptoms stated above and may also use testing to rule out the following diagnosis:
- Sacroiliac joint syndrome
- Internal disk disruption syndrome
- Lumbar spondylolisthesis and spondylosis
- Chronic Pain syndrome
- Lumbar compression fracture
- Overuse injury
- Fibromyalgia
- Mechanical low back pain
- Coccyx pain
- Deep infection
- Herniated disks
- Fractures of the spine
- Torn muscles
- Acute intra-abdominal problems(1,3)
There are a couple studies that can be done to help determine facet arthropathy and disregard the above diagnosis. They consist of the following:
- MRI Magnetic resonance imaging scans
- Diagnostic blocks
- CT scan
- X-rays (1,3)
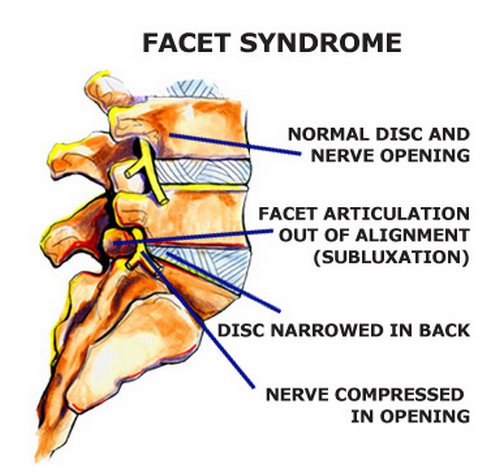 Picture 3 : A clear depiction of the lumbar spine which has faucet articulation issues.
Picture 3 : A clear depiction of the lumbar spine which has faucet articulation issues.
Photo Source : naturalcuredoctor.com
What Causes Facet Arthropathy?
There could be many causes noted and each of these causes having their specific initiation point. The following is not a comprehensive list of possible causes for facet arthropathy:
- Microtrauma
- Osteoarthritis
- Synovial capsule distention and inflammation
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Wear and tear
- Excessive lifting
- Poor posture
- Poor body mechanics when lifting or bending
- Obesity
- Sports that cause overuse (1,3,4)
Locations for Facet Arthropathy
Facet arthropathy can be found in the neck or in the back. If it is noted in the neck joints it is called cervical facet arthropathy. In the case that it is the lower back it would be called lumbar facet arthropathy.
Sometimes the specific vertebrae affected will be noted as part of the diagnosis and may appear as the following:
- Facet arthropathy l5-s1
- Facet arthropathy L2
- Lumbar facet joint
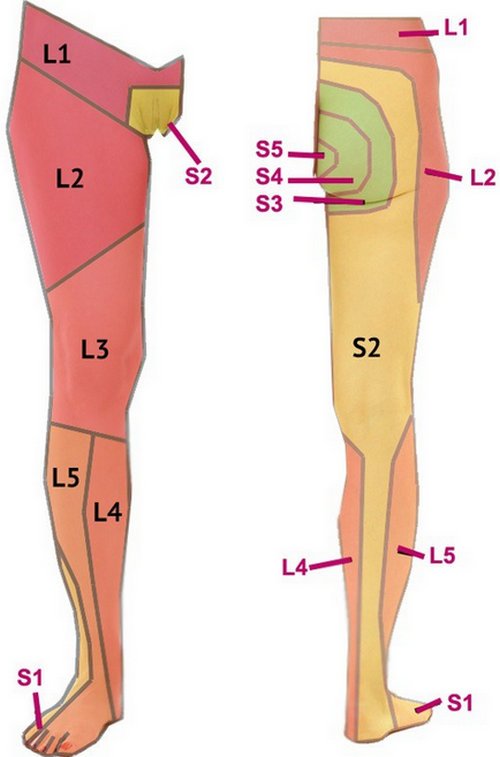
Image 4 : In this image, the spinal areas are marked by their names.
Picture Souece : www.simplebackpain.com
Types of Facet Arthropathy
Lumbar facet arthropathy
Lumbar facet arthropathy is the degeneration of the lumbar joints. This could be called L1-L5 as mentioned in the above section. This is due to poor body mechanics and can radiate to the areas noted in the above picture.
Cervical facet arthropathy
Cervical facet arthropathy is degeneration in the joints of the neck area. This could be called C1-C7. This could have many causes ranging from poor body mechanics to blunt trauma injury. This pain could radiate into the arms and chest.
Degenerative facet arthropathy
Degenerative facet arthropathy is just another way to describe the actions taking place with facet arthropathy. It may be used as a full in depth diagnosis.
Hypertrophic facet arthropathy
Hypertrophy is the increase of an organ or area of the body which is abnormal. In this situation it would be a section of the facet joint. This will cause pain in the area near the specific joint affected.
Bilateral facet arthropathy
Bilateral means both side, knowing this helps explain that bilateral facet arthropathy means that the degeneration is happening to both sides of the joint.
Thoracic facet arthropathy
thoracic facet arthropathy is degeneration in the joints of the thoracic (chest or upper back) area. This could be detailed as T1-T12 and can cause radiating pain to the arms, chest, and lower back. (1, 2, 6, 7)
Treatment
Surgical intervention is not needed for facet arthropathy. The following are other options of treatment. T(1,3)
Medications
Opioids
- Tramadol
- Codeine
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
- Gabapentin
- Pregabalin
- In severe cases – morphine (5)
Facet joint injections
- Steroid injections
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Intra-articular joint injection (1)
- This link leads to a video which vividly explains the joint injections: http://www.spine-health.com/video/facet-joint-injections-procedure-video (3,5)
Facet joint Arthropathy exercises
Physical therapy
- Traction
- Behavioral modification (9)
- Good posture is always helpful
- Heat applications
- Changes in routines
- Sometimes anti-inflammatory medications can help with the pain. (3,5)
Prevention
Facet arthropathy is normally considered a mechanical problem due to misuse of the joints. The best prevention is as follows.
- Good posture while sitting or standing
- Proper body mechanics while lifting or bending
- Maintaining flexibility through exercise
- Flexion
- Extension
- Stretching (9)
Eating a healthy diet which includes
- Good source of calcium
- Good source of vitamin D
Exercise which increases strength in the back
- aerobics (9)
Risk factors for Facet Arthropathy
There have been no studies to show that race or sex have any risk factors for facet arthropathy. Although some studies do show that age can cause significant risk. This study showed 18% chance of people between the ages of 31-40 and 44% change in people between the ages of 51-60. (1)
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the various treatments, causes, and prevention of facet arthropathy. The best way to prevent and help with pain due to facet arthropathy is proper posture and healthy lifestyle. Be sure to always seek medical attention if the pain is severe.
References:
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/310069-overview
- http://www.mayo.edu/pmts/mc5500-mc5599/mc5520-0116.pdf?_ga=1.18379641.1717306767.1484667538
- http://www.spine-health.com/conditions/arthritis/symptoms-and-diagnosis-facet-joint-problems
- https://www.laserspineinstitute.com/back_problems/facet_disease/articles/facet_joint_arthropathy/
- http://prc.canadianpaincoalition.ca/fr/facet_arthropathy.html
- http://www.fmcpaware.org/h-l/lumbar-facet-arthropathy
- https://www.reference.com/health/severe-facet-arthropathy-958b8055916b1907
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arthropathy
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Back_Pain/default.asp#4
- Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation By Walter R. Frontera, Julie K. Silver, Thomas D. Rizzo Jr. https://books.google.com.mx/books?id=1sXsAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA233&dq=facet+arthropathy&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=facet%20arthropathy&f=false
- Atlas of Image-Guided Intervention in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine By James P. Rathmell https://books.google.com.mx/books?id=DZhSxcok7poC&pg=PA82&dq=facet+arthropathy&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=facet%20arthropathy&f=false
