What is Odynophagia? Definition
Odynophagia is a medical term for painful swallowing. It is often confused with the term dysphagia, which means difficulty swallowing. With odynophagia, the patient complains of pain when trying to swallow.
The pain can be felt in the mouth, throat, and/or esophagus. If the patient complains of pain when swallowing, it is an indicator that something is not right in the body. It is important to consult your doctor so that the underlying cause will be determined and the patient will be able to receive the appropriate treatment. (1, 2, 3)
Photo 1: A painful throat is an indicator of a painful swallowing (odynophagia).
Image Source: diseasespictures.com
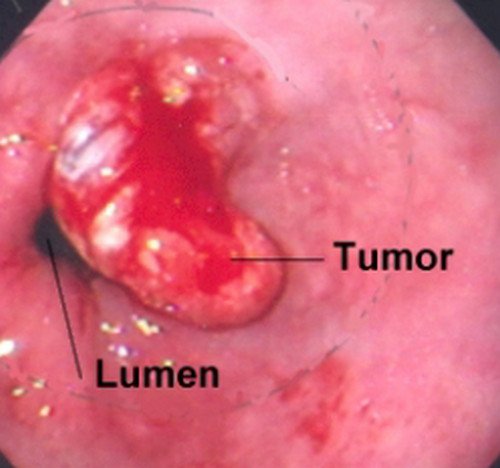
Picture 2: A tumor in the esophagus, which is one of the reasons for painful swallowing.
Photo Source: yoursurgery.com
Odynophagia Causes
- Cancer – When a patient complains of chronic painful swallowing, the doctor will rule out esophageal cancer. The tumor develops in the esophagus. There are various reasons why tumor develops in the esophagus such as alcohol abuse, chronic smoking, and persistent heartburn. In rare instances, esophageal cancer can be hereditary.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – the lower sphincter in the esophagus is not closing properly. This causes the stomach acid to leak back into the esophagus. One of the symptoms of GERD is painful swallowing, chest pain, and heartburn. (3)
- Candida infection – This fungal infection can affect the mouth. It will spread and affect the esophagus. That’s why patients with candida infection complain of painful swallowing.
- Ulcers – They are sores that can affect the oral cavity particularly the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach. Factors that can increase the risk of ulcers are a chronic use of anti-inflammatory drugs and untreated Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- HIV – People with HIV are immunocompromised. They are prone to infection. The retroviral drugs used to treat HIV can increase the possibility of painful swallowing. (4)
- Side effects of treatment – Some forms of treatment can cause painful swallowing such as radiation therapy for cancer and side effects of prescription medications.
- Object stuck in the throat – Small sharp objects stuck in the throat can significantly affect your ability to swallow. It causes painful swallowing. (4, 5)
Difference between dysphagia and odynophagia
These two medical terms are somewhat related that’s why a lot of people used it interchangeably. However, odynophagia is different to that of dysphagia.
Dysphagia is when a person experiences difficulty in swallowing. The swallowing difficulty can occur on a regular basis and is common in older people. Not all people with swallowing difficulties experienced pain.
If you have difficulty swallowing but don’t have any pain at all, then the condition is called dysphagia. On the other hand, odynophagia is the term used to describe a painful swallowing. (5, 6, 7)
Odynophagia Symptoms
- Pain when swallowing
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the oral cavity that intensifies when a person tries to swallow
- The patient complains of globus sensation. What is the globus sensation? It is the feeling of having a lump or obstruction in the throat when there is really none. (7, 8)
Diagnosis
Endoscopy is the commonly used procedure to diagnose odynophagia. A small lighted camera (endoscope) is placed in the throat so that the doctor can visualize the esophagus. The doctor will also ask you to swallow during the procedure.
Other tests will be ordered to accurately diagnose the underlying cause of odynophagia.
Odynophagia Treatment
Odynophagia treatment guidelines include the following:
- Drug therapy – depending on the underlying cause, the doctor will prescribe medications such as medications for GERD to prevent stomach acid to go back into the pharynx and esophagus. The medicines are used to target the underlying cause of odynophagia. If it is caused by candida infection, then an antifungal agent should be used.
- Surgical approach – if the cause of painful swallowing is a tumor, the doctor will perform a surgical procedure to get rid of the tumor cells. If you have GERD and the condition does not improve despite aggressive drug therapy, then the doctor will perform surgery for GERD.
- Time – If there is no underlying cause for odynophagia, then maybe you should give it some time to resolve on its own. Painful swallowing is common, especially after severe allergies or cold. When the infection completely goes away, your swallowing will improve significantly. (4, 9, 10)
Outlook
Many underlying health conditions for odynophagia will significantly improve if detected and treated early. If you are experiencing swallowing difficulty, then you should inform your doctor the soonest time possible.
If the condition is left untreated, it could lead to more serious complications. If you have a painful swallowing, your eating habit will be affected. You will eventually lose weight. The body will not receive the nourishment it needs. It could lead to dehydration, malnutrition, and anemia. It could also make you susceptible to different types of illnesses. (3, 4)
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Odynophagia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/odynophagia
- http://www.healthhype.com/swallowing-pain-causes-of-odynophagia-painful-swallowing.html
- http://www.clinicaladvisor.com/hospital-medicine/dysphagia-and-odynophagia/article/600672/
- https://www.doctorshealthpress.com/health-articles/odynophagia-painful-swallowing/
- http://www.ehealthstar.com/painful-swallowing-odynophagia.php
- https://www.medicalopedia.org/911/dysphagia-vs-odynophagia/
- https://heydoctor.org/odynophagia.html
- https://www.singhealth.com.sg/PatientCare/ConditionsAndTreatments/Pages/odynophagia-pain-on-swallowing.aspx
- http://www.medicotips.com/2013/04/why-painful-swallowing-odynophagia.html
