The prostate is a gland anatomically situated in between the bladder and the penis. Its size is similar to that of the walnut. Its shape is similar to that of the rounded cone and the base points toward the bladder.
It is both a muscular and a glandular structure. The prostate has ducts that open into the prostatic area of the urethra. It has three lobes, one in the middle and the other two on both sides. (1, 2, 3)
Prostate gland anatomy
The prostate’s anterior end contains two lateral lobes that are round in shape. When viewed transversally, the prostate looks like orange slices. In the posterior part of the lateral lobe is a much smaller lobe containing fibromuscular tissues, which contract during ejaculation.
Another significant structure if the median lobe containing ejaculatory ducts. On the other hand, the posterior lobe creates a thin layer of tissues. (2, 3, 4)
Where is the prostate located
The prostate is in the middle of the pelvis just about two inches in and toward the belly. It is about two to three inches in the male rectum. The prostate gland size is similar to that of the walnut and chestnut. Its weight is between 20 grams to 30 grams. (4, 5)
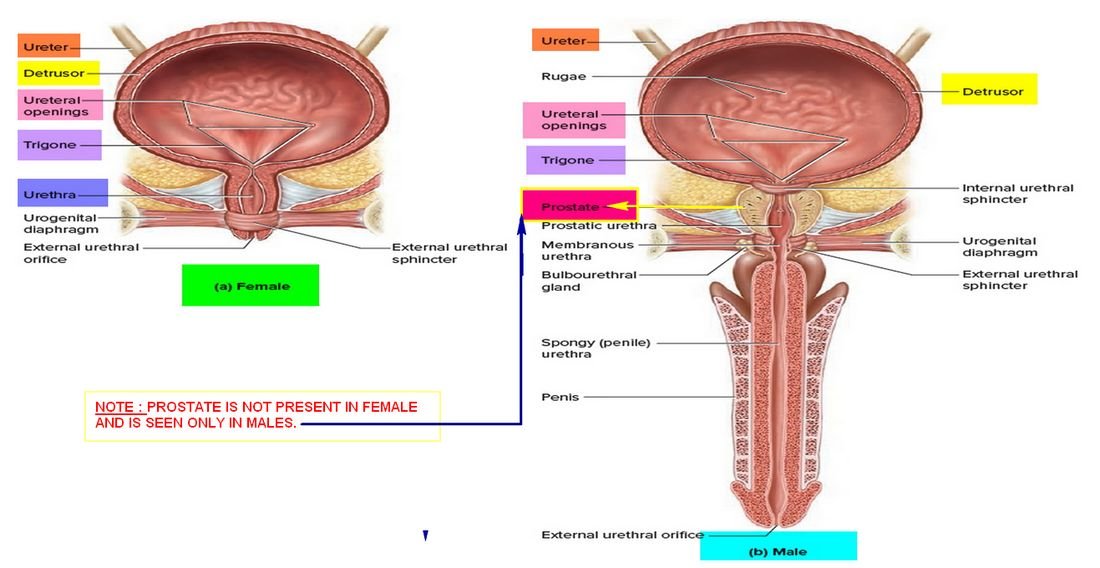

Image 1: The male reproductive system with emphasis of the prostate gland.
Picture Source: img.webmd.com
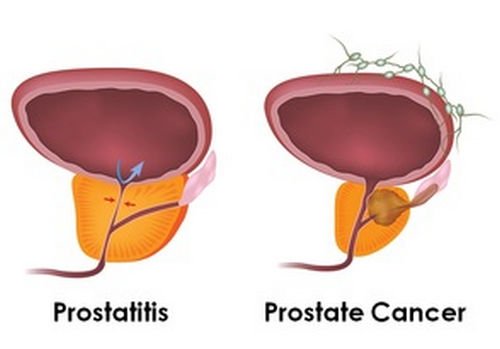
Picture 2: A comparison image between a normal/healthy prostate and prostate cancer.
Photo Source: www.mvpchiro.com
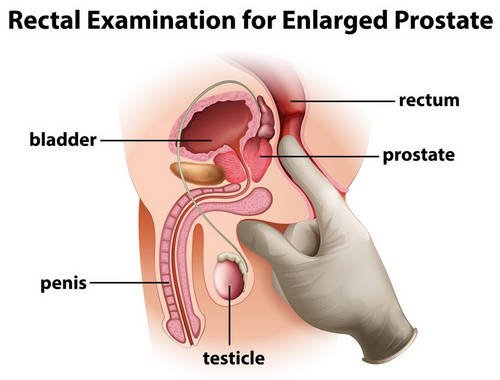
Photo 3: A rectal examination to detect an enlarged prostate.
Image Sourcce: www.naturalcolonrx.com

Image 4: A comparison image of a healthy and inflamed prostate.
Picture Source: www.sweet-cures.com
Tissues in the prostate gland
There are two types of tissues in the prostate gland. These are the fibromuscular tissues and exocrine glandular tissues.
- Fibromuscular tissue – It is a combination of the smooth muscle tissues and dense irregular connective tissues. It contains collagen fiber that provides strength to the tissues. The smooth muscle allows the tissue to contract so as to expel the fluid during ejaculation. The fibromuscular tissues are found in the outermost layer of the prostate gland.
- Exocrine glandular tissue – It is an epithelial tissue responsible for the secretion of semen. Majority of the prostate consists of exocrine glandular tissue. (3, 4, 5, 6)
What are the functions of the prostate gland?
- The prostate gland is a part of the male reproduction system. Its function is to help secrete a fluid that is part of the seminal fluid (carrying the sperm). During the ejaculation process, the prostate propels the fluid into the urethra.
- The prostate produces a prostatic secretion, which is a milky mixture of sugars, specifically glucose and fructose, enzymes, and alkaline chemicals. The sugar provides nourishment to the sperm while the enzymes help break down essential protein in the semen. The alkaline material neutralizes the acidic vaginal environment thereby helping the sperm to make it through during implantation.
- The prostate gland has an ejaculatory duct that facilitates the release of sperm during ejaculation. The duct opens and the smooth muscle tissues in the prostate contract enabling the semen to freely pass into the urethra.
- The prostate plays an important role in male’s fertility. It has a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) that enables the sperm to swim into the uterus.
- Prostate gland does a wonderful job of achieving sexual satisfaction. The pumping action of the prostate gland produces a very good feeling making sex more desirable and pleasurable.
- The prostate gland is the male’s sexual pleasure spot, an equivalent of G spot in the female. Stimulation of the prostate produces a strong sexual response and intensifies the orgasm.
- The nerves in the prostate help in achieving and maintaining an erection. Prostate erection nerves facilitate swelling and hardening of the penis.
- Prostate gland filters and facilitates removal of toxins. It protects the sperm and increases the chances of impregnation.
- A healthy prostate gland reduces the possibility of urinary infection. It is the reason why men are less susceptible to urinary tract infection than women.
- Prostate gland helps in regulating the production of the male hormone testosterone. The prostate gland has a 5-alpha-reductase enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT. (5, 6, 7, 8)
Prostate Gland Problems
As men grow older, problems in the prostate gland start to appear. It is common in men 50 years old and above, which is why health care professionals strongly suggest that older men should undergo PSA test every year. Common prostate gland problems include:
Prostatitis
It is the inflammation of the prostate secondary to infection. It is usually treated using antibiotics.
Enlargement of the prostate/benign prostatic hypertrophy
It is the abnormal growth of the prostate gland, which is a common condition in older men. Prostate gland enlargement symptoms include difficulty urinating, urine urgencies, especially at night, dribbling after urinating.
The patient is put on a drug that can help shrink the prostate. If the condition is already in the advanced stage, the best thing to do is to perform surgical procedures.
Prostate cancer
It is one of the common forms of cancer in men. What are the 5 early warning signs of prostate cancer? These are frequent painful urination that may contain blood, erectile dysfunction, inability to control the bladder, lower back pain, and decreased semen during ejaculation. What makes you susceptible to prostate cancer? Men older than 50 years old are prone to prostate cancer.
The prevalence is high in African-American men. If any of your immediate family members have had a prostate cancer, then there is a possibility that you can have it too. Don’t you know that your diet can account for the formation of prostate cancer? A high-fat diet makes you susceptible to prostate cancer.
The treatment approach for prostate cancer varies depending on the extent and severity of the condition. If it is in the early stage, a radiation and chemotherapy are used to kill the cancer cells. The body will be hindered from producing testosterone so as to prevent recurrence. Hence, the patient needs to be put in a hormone therapy. Lastly, a surgical removal of the prostate can be done when deemed necessary, especially if the entire prostate is involved. (6, 8, 9, 10)
What happens when you have your prostate removed?
If the prostate is surgically removed, the patient could have urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
References:
- https://www.webmd.com/urinary-incontinence-oab/picture-of-the-prostate#1
- https://www.emedicinehealth.com/enlarged_prostate/article_em.htm#what_causes_an_enlarged_prostate
- https://www.livescience.com/32751-what-does-the-prostate-gland-do.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate
- https://www.macmillan.org.uk/information-and-support/prostate-cancer/early-prostate-cancer/understanding-cancer/the-prostate-gland.html
- https://prostate.net/articles/10-amazing-functions-of-the-prostate-gland
- http://www.kidneyurology.org/Library/Urologic_Health.php/Prostate_Enlargement.php
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/prostate-gland-and-urinary-problems
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/prostate-problems
- https://universityhealthnews.com/daily/prostate/what-is-the-prostate-gland/
