What’s Abdominal Pain?
Abdominal pain is a frequent reason for consultation especially in young adults and elderly subjects.
It is a symptom rather than a disease. The causes of pain may range from mild, non-significant, exaggerated peristalsis to emergent appendicitis or perforation. At times, abdominal pain may be the only symptom of heart attack.
Therefore, due care must be lent to patients who present with a symptom of abdominal pain. For easier identification of the organ/s from which pain arises, abdomen is divided into different regions. Abdominal divisions are called quadrants, though these are nine in number. Each quadrant contains specific organs that can produce pain. [1], [2] [and] [3]
Abdominal pain can be diffused in nature in conditions like peritonitis and intestinal obstruction. It may also be localized in conditions for which causes depend on the exact location of pain.
Also see : Location and Pictures of Different organs in the Abdomen
Classification
a) Diffuse Pain
1) Peritonitis
It is an inflammation of the peritoneum, which forms a protective layer to abdominal organs. It occurs most commonly in the elderly due to perforation of an ulcer and in a female d/t rupture of ectopic pregnancy. It’s a surgical emergency.
Diagnosis
Mostly clinical, erect x-ray confirmation
Treatment
Surgery
2) Intestinal Obstruction
It is the obstruction to passage of food within the lumen of the intestine. Obstruction can be internal, as in cases of polyp, hard feces, malignancy. It can also be external, as in cases of intestinal bands, torsion, volvulus.
Diagnosis
Erect x-ray, UCG, CT, barium enema, barium follow-through
Treatment
Relieving the obstruction is of prime importance. After that, address the primary cause.
3) Volvulus
It is twisting of intestine on a narrow base. Volvolus is most commonly observed in neonates and elderly. In neonates, it is more common in the small intestine and right colon while in adults, it is most common in the sigmoid colon.
Diagnosis
Erect x-ray, USG
Treatment
Surgery
b) Localized Pain
For this we will theoretically divide the abdomen to three regions: right side, left side and the central part.
Each region will be divided into smaller regions called quadrants; each quadrant has specific pathologies associated with, but a unique pathology can cause pain simultaneously in different regions. [12]

Picture : The regions of abdomen: Nine abdominal quadrants
Image source : health.usf.edu
What is Right Side Abdominal Pain?
Right side abdominal pain is pain felt in the right hypochondriac region, right lumbar region, and right iliac region.
The right hypochondriac region contains: liver (right lobe), gallbladder, hepatic duct, and right colic angle.
The right lumbar region contains the ascending colon and the right kidney when cecum and appendix lie in the right iliac region. [12]

Picture of Right side abdominal pain with various causes and location
Causes of Right Side Abdominal Pain
As explained earlier, causes vary from a quadrant to another, so we will treat each abdominal region separately.
In the right hypochondriac quadrant, the main causes of pain are hepatitis, cholecystitis, gallstones, pyelonephritis, colitis, and right kidney stones. [1] To [9]
1) Hepatitis
Diagnosis:
Viral serology (HBV, HCV), Autoimmune antibodies
Treatment:
Antiviral drugs, Corticoids
2) Cholecystitis and Cholangitis
Acute inflammation due to a stone in gall bladder and bile duct are called cholecystitis and cholangitis, respectively. Cholecystitis is more common in fertile, fatty females in their forties (4Fs).
Diagnosis
- MRCP, ERCP, Abdominal ultrasonography
Treatment
- Cholecystectomy

Cholecystitis pain location picture
image source: drugs.com
3) Pyelonephritis
It is an acute and severe kidney infections that can alter the renal function and cause extreme abdominal pain.
Diagnosis
- Urine culture (CEBU)
Treatment
- Antibiotics
4) Colitis
Colitis is the inflammation of the colon. It can be infectious, iatrogenic (caused by drugs), ischemic, or caused by radiotherapy.
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy
Treatment
- Corticoids, aminosalicylates, immunomodulator medicines
5) Right Kidney Stones
Stones in renal pelvis may give rise to pain in right hypochondriac region but when this stone slips into the ureter, its presentation varies greatly depending on the position of stone.
- Stone in upper 3rd – pain in testis
- Stone in middle 3rd – pain at iliac region
- Stone in lower 3rd – pain in inner aspect of thigh
Diagnosis
- Renal ultrasonography, CT scan
Treatment
- Ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy, surgery
When you feel pain in the right lumbar region you may have diverticulosis (multiple hernias of the mucosa through the muscular wall of the colon), colitis or right kidney stones. [1] To [9]
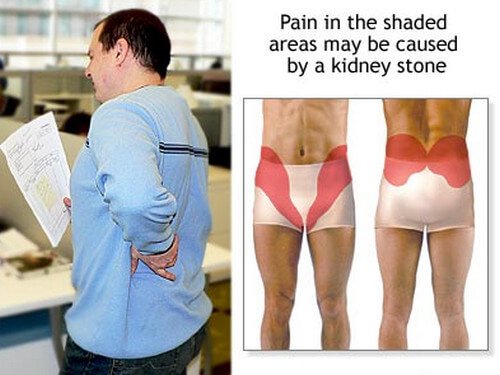
Kidney stone pain location picture
Image source : ADAM Inc
The main pathologies that can hurt in the right iliac region are appendicitis and genital causes (ovarian cancer or cysts, salpingitis, ectopic pregnancy) in women. [1] To [9]
1) Appendicitis
Pain in Appendicitis
Pain typically occurs around the umbilicus at its onset and gradually shifts to McBurney’s point. McBurney’s point is the junction of lateral one third and medial two third of a line joining anterior superior iliac spine to umbilicus.
Note: Counterpart of McBurney’s point on left side is Sir Philip Manson–Bahr amoebic point seen in amoebic pancolitis.
Diagnosis
- The diagnosis is clinical but can be helped by Complete Blood Count (CBC) and abdominal ultrasonography.
Treatment
- Appendectomy

Appendicitis pain location (progression of pain) from periumbilical region to lower right
Image source : zadehsurgical.com
2) Genital Causes in Women
Ovarian cancer or cysts: benign or malignant tumors developed in a woman’s ovaries.
Diagnosis
- Pelvic ultrasonography, CT scan, MRI.
Treatment
- Surgery
3) Salpingitis
Diagnosis
- Pelvic ultrasonography, Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Treatment
- Antibiotics
4) Ectopic Pregnancy
Diagnosis
- Ultrasonography, beta-hCG measurement.
Treatment
- Methothrexate, surgery
Right Side Abdominal Pain in Children
The diagnosis of abdominal pain in children can be very difficult because they cannot show their emotions mainly if they are still too young. In such cases the pain will cause the child to cry all the day and make him refuse feeding. These signs should attract the parents’ attention to consult a doctor immediately. [13]
The main causes of Right Side Abdominal Pain in children can be divided into :
A) Digestive causes
1) Baby Colic
Babies can cry all the time without any real cause.
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
Treatment
- Comforting your baby
2) Gastroenteritis
Diagnosis
- Clinical Diagnosis, vomiting, diarrhea…
Treatment
- Healthy diet, antidiarrheal and antiemetic drugs, antibiotics
3) Cow’s Milk Allergy (CMA)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
Treatment
- Remove cow’s milk
B) Surgical causes
1) Acute Intussusception
This is an extremely severe disease in which a part of your baby bowel gets inside another one causing extreme pain.
Diagnosis: Abdominal ultrasonography
Diagnosis
- Abdominal ultrasonography
Treatment
- Barium enema, Surgery
2) Bowel Obstruction
Diagnosis
- CT-scan, MRI
Treatment
- Antibiotics, Surgery
3) Bowel Volvulus
Diagnosis
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA)
Treatment
- Surgery
4) Strangulated Hernia
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
Treatment
- Surgery
5) Digestive Duplication
An abnormal copy of an intestinal segment.
Diagnosis
- CT scan, MRI
Treatment
- Surgery
6) Other causes that make pain by general infection mechanisms
- ENT infections: otitis, sinusitis.
- Pulmonary infections.
- Urinary tract infections.
What is Central Abdominal Pain
Central abdominal pain is pain located in one of these three quadrants: Epigastric region, umbilical region and finally hypogastric quadrant.
The epigastric region contains the duodenum, a portion of the liver, the pancreas and a portion of the stomach, while the umbilical quadrant contains the transverse colon and the duodenum.
In the hypogastric quadrant lie the small intestine, bladder and the uterus.[12] Picture of central abdominal pain with various causes and location
Picture of central abdominal pain with various causes and location
Image source : manchestergeneralsurgery.com
Causes of Central Abdominal Pain
The main causes of pain in the epigastric region are [1] To [9]
1) Esophagitis
Esophagitis is manifested by pain in the epigastric region and extending upwards into retrosternal region. It is typically expressed as burning pain. This is most commonly seen in alcoholics and smokers aggravated by spicy foods.
Diagnosis:
Esophagoscopy, 24hr pH monitoring
Treatment:
Proton pump inhibitors, antacids
2) Stomach Ulcer
Diagnosis
- Endoscopy
Treatment
- Proton pump inhibitors PPI, antacids.
3) Duodenal Ulcer
Diagnosis
- Endoscopy
Treatment
- Proton pump inhibitors PPI, antacids
4) Stomach Cancer
Diagnosis
- Endoscope guided gastric biopsy, transesophageal ultrasonography
Treatment
- Gastrectomy
5) Gastritis
Gastritis refers to the chronic inflammation of stomach mostly because of Helicobacter pylori infection but can also be due to NSAID abuse, alcoholism, and smoking.
Diagnosis
- Endoscopy, gastric biopsy
Treatment
- Antibiotics, Proton pump inhibitors, antacids
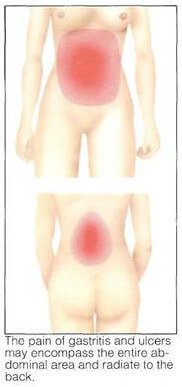
Picture : Location of Gastritis and Ulcers pain : these conditions encompass the entire abdominal are radiate to the back
6) Pancreatitis
- In this condition, pain usually begins gradually or suddenly in the upper abdomen and it can sometimes extend to the back.
- Initially, it is mild and it can be worse after eating.
- Mostly chronic pancreatic pain is experienced in the upper abdominal region, although there may not be any pain for some people.
- Pain can spread to back, and also feel worse when drinking and eating.
- Abdominal pain disappears as the condition worsens, because the pancreas is not capable of producing digestive enzymes anymore.
Diagnosis
- Pancreatic enzymes, CT scan, MRI
Treatment
- Analgesics, intravenous fluid, Nil Per OS

Pancreatitis pain location picture
7) Pancreatic Cancer
Diagnosis
- CT scan, MRI
Treatment
- Surgery, chemotherapy
8) Gallstone in the common bile duct
Diagnosis
- MRCP and ERCP
Treatment
- ERCP is both diagnostic and therapeutic, Cholecystectomy
9) Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Myocardial infarction involves an acute ischemia in a part of cardiac muscle. It may be due to atherosclerotic occlusion of blood vessels supplying the heart.
Pain in Myocardial Infarction
Pain in myocardial infarction is of squeezing in quality and patient explains episode of pain by keeping a clenched hand in front of chest (Levine sign). The extreme pain or tingling sensation may radiate to the inner aspect of left upper limb. Episodes of pain may be associated with sweating or palpitation.
Diagnosis
ECG, cardiac enzymes
Treatment
Thrombolysis, percutaneous coronary intervention, coronary bypass surgery
Pain located in the umbilical region can be caused by
1) Gastroenteritis
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis: vomiting, diarrhea.
Treatment
- Healthy diet, antidiarrheal and antiemetic drugs, antibiotics
2) Volvulus of the small bowel
Diagnosis
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA)
Treatment
- Surgery
3) Crohns’ Disease
Called also inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), its main symptoms are abdominal pain that worsens after eating and chronic diarrhea.
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy
Treatment
- Corticoids, immunomodulator medicines.
4) Digestive Parasitosis
Diagnosis
- Stool ova and parasites exam
Treatment
- Antiparasitic drugs
5) Colitis
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy
Treatment
- Corticoids, aminosalycilates, immunomodulator medicines.
Finally, if you feel hurt in the hypogastric region, you may have:
1) Cystitis
Diagnosis
- Urine culture CBEU
Treatment
- Antibiotics
2) Genital causes in women (diseases of the uterus).
What is left side Abdominal pain?
As explained earlier, we split the whole abdomen to three wide regions.
Left side abdominal pain occurs when you feel hurt in one of these quadrants: the left hypochondriac region, the left lumbar region, and the left iliac region.
The left hypochondriac region contains: Spleen, a part of the stomach and the left colic angle. The left lumbar region contains the descending colon and the left kidney when sigmoid colon lies in the left iliac region. [12]

Picture of Left side abdominal pain with various causes and location
Image source : manchestergeneralsurgery.com
Causes of Left Side Abdominal Pain
We will mention causes quadrant by quadrant, and begin with the left hypochondriac regions where pain can be mainly caused by ruptured spleen (spleen will be broken into small parts and threatens your life), colitis, diverticulosis, pyelonephritis or urinary calculi of the left kidney. Also see : Spleen location and anatomy
When you feel pain in the left lumbar region you must first think about left kidney stones and colitis. [1] To [9]
Pain in the left iliac region is mainly caused by
1) Sigmoiditis
Diagnosis
- Sigmoidoscopy
Treatment
- Corticoids, aminosalycilates, immunomodulator medicines.
2) Acute or Chronic Constipation.
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
Treatment
- Diet and laxatives
3) Ulcerative Colitis
It is the inflammation of colon occurring continuously from rectum and moving more proximally. It only involves the mucosa and submucosa. The patient is predisposed to dysplasia and colon cancer even more than Crohn’s Disease.
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy
Treatment
- Corticoids, aminosalicylates, and immunomodulator medicines followed by left hemicolectomy
4) Crohns’ Disease
Just as ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease is also an inflammation of the colon and is differentiated from ulcerative colitis by its skip like pattern of involvement and involving whole thickening of bowel wall. It predisposes the patient to fistula even more than ulcerative colitis.
NOTE: The term inflammatory bowel disease encompasses both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy
Treatment
- Corticoids, immunomodulator medicines, and total colectomy
5) Genital Causes in Women
Kidney Pain
Kidneys exist in both sides of your body, they lie in the lumbar fossa towards the back of your body; they are protected by the lower ribs.
Left kidney is higher than the right. Pain generated by kidneys is usually located in the lower back but can extend into testicles.Also see : What side is your appendix on [10] [and] [11]
Kidney Pain Causes
- Kidney stones: the origin of the pain is the sudden obstruction of the urinary tract.
- Pyelonephritis: an infection of urine in the kidney.
- Polycystic kidney disease: a genetic disease characterized by the presence of cysts or renal tumors inside the kidney, these tumors can be benign or malignant.
- Renal ischemia: due to the obstruction of the renal artery caused by atherosclerosis.
- Kidney tumors: abnormal cellular growth inside your kidney, they can be benign or malignant.
- Renal vein thrombosis: the occlusion of the renal vein generally caused by metastases and bleeding disorders.
- Hydronephrosis: is the result of retention of urine due the obstruction of the ureter.
Kidney Pain Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the pain itself is easy; kidney pain usually begins in the back and round the side toward the thigh and genital organs. [11] [and] [12]
The diagnosis of the pain cause varies depending on the causal pathology
1) Kidney Stones
Big stones can be diagnosed by usual abdominal x ray but the best exam to detect stones is CT scan.
Treatment
- Ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy, surgery
2) Pyelonephritis
- The main diagnosis method is urine culture CBEU.
Treatment
- Antibiotics
3) Polycystic Kidney Disease
Treatment
- Blood pressure drugs, diuretics, low-salt diet
4) Renal Ischemia
Treatment
- Surgery
5) Kidney Tumors
Main diagnosis methods are MRI, CT scan and renal biopsy.
Treatment
- Chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery
6) Renal Vein Thrombosis
Both renal Doppler and CT scan can be used.
Treatment
- Anticoagulation therapy
7) Hydronephrosis
Can be easily diagnosed by renal ultrasonography.
Treatment
- Removal of the obstruction and urine drainage
General Causes of Abdominal Pain
This is most commonly seen in the setting of neglected renal stone causing obstruction. [1] to [9]
Parietal Causes
- Contractures after doing exercise
- Acute fever (flu, flu syndrome).
Widespread abdominal pain caused by
- Peritonitis: severe abdominal infection that spreads all over the abdominal cavity.
- Ulcerative colitis: when colitis progress in time it can be ulcerative and make terrible pain feeling.
- Mesenteric infarction: ischemic intestinal lesions that produce intense pain sensation.
- Intense anxiety and depression that can create unreal pain feeling.
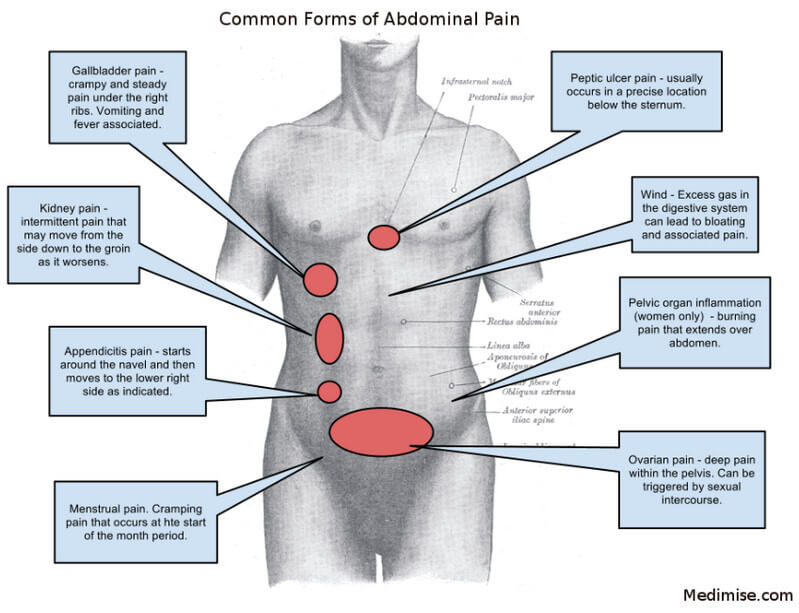
Picture : Locations of pain caused by some Abdominal organs
- Appendicitis pain location – starts around the navel and then moves to the lower right side as indicated
- Menstruation pain location – Cramping pain that occurs at the start of the month period in the area shown in the above picture.
- Ovarian pain location – deep pain within the pelvis.
- Pelvic organ Inflammation location (women only) – burning pain that extends over abdomen.
- Peptic ulcer pain location – usually occurs in the precise location below sternum (most often confused with heart pain)
- Gallbladder pain location – crampy and steady pain under right ribs. Fever and vomiting are associated with it. Also see : Gallbladder location and anatomy
- Kidney pain location – intermittent pain that may move down from the side down to the groin as it worsens.
Image source : Medmise.com
What is Referred pain ?
Is pain felt in a location far away from the suffering organ causing the pain, it is due to neuron intersections in the central nervous system.
Treatment for Abdominal Pain?
Like any other symptom, Abdominal Pain can be healed in 2 ways: [6]
1) Symptomatic treatment
In symptomatic treatment our objective is to reduce the pain feeling without treating its real cause, many drugs and methods can be used
a) Drug-based treatments
- There are many drugs used to reduce the pain feeling called analgesics.
- Analgesics vary in their pharmacological power from level 1 analgesics used for mild pain to narcotics used for severe pain.
- Physical treatments – Like physiotherapy, physical therapy (application of heat, cold, or electricity) and massage.
- Surgical treatments – Anesthetic treatment.
- Neurostimulation – To apply to the painful region a low intensity electrical current to heal.
- Hypnosis – Reduce pain sensation by changing the perception of the outside world by the patient.
2) Radical treatment
The pain is totally eliminated by treating the pathology causing it. Examples are appendectomy for appendicitis, and antibiotics for gastroenteritis.
Disclaimer : Follow your doctor instructions for the treatment; this is for informational purpose only.
Reviewed by : Dr. Jagadesh Madireddi
Proofread by: Dr. Jackie Te
References
http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/guide/abdominal-pain-causes-treatments
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abdominal_pain
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003120.htm
http://www.medicinenet.com/abdominal_pain/article.htm
http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/diseases/facts/abdominalpains.htm
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/abdominal_pain_in_adults/article_em.htm
http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticles.nsf/pages/Abdominal_pain_in_adults
http://alldisease.blogspot.com/2006/04/abdominal-pain.html
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/abdominal-pain/MY00390
http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/KUDiseases/pubs/stonesadults/index.aspx
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/kidney-pain/MY00125/DSECTION=causes
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abdomen
http://www.aafp.org/afp/2003/0601/p2321.html
Please note : It is very difficult to make this topic but still I tried my best to gather authentic information from various medical books and online sources to help people understand this complicated and vast topic. If you find any mistakes or any corrections, please contact us ASAP and we will rectify it ASAP. Thanks !

